Pressure Drop Calculations
Calculating pressure drop in piping systems is a crucial aspect of engineering design. It helps in understanding the hydraulic performance of a pipeline and ensuring the system operates efficiently. The following steps outline the method to calculate pressure drop in a piping system based on ASME standards.
Steps for Piping Pressure Drop Calculations
1. Define Parameters of the System

2. Determine Flow Rate

3. Calculate Flow Velocity
Using the flow rate, calculate the fluid velocity in the pipe:

4. Calculate Reynolds Number

Note:

5. Determine the Friction Factor
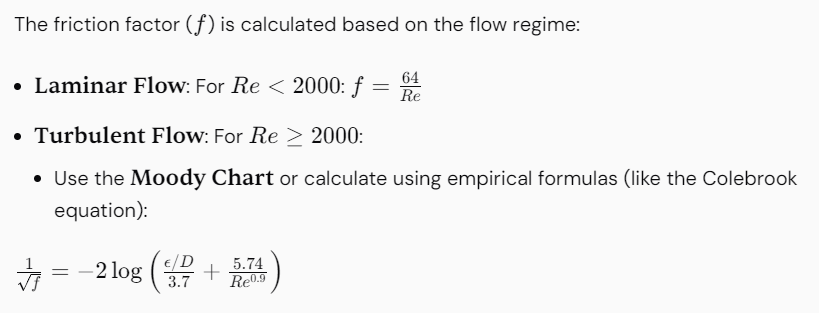
Where:

6. Calculate Pressure Drop in the Pipe

7. Include Additional Losses (if applicable)
Consider fittings, bends, valves, and other components in the piping system that contribute to pressure drop:
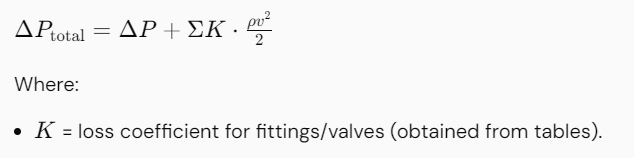
8. Calculate Total Pressure Drop
Add up the pressure drop from the straight pipe and all additional components to find the total pressure drop across the entire system.
Summary
The calculation of pressure drop in piping based on ASME standards involves understanding fluid properties, determining the flow regime, calculating friction factors, and applying the Darcy-Weisbach equation. Additional losses due to fittings and other components should also be considered. Always refer to relevant reference materials and standards for specific guidelines. This method will provide the necessary calculations to ensure efficient system design and operability.